Skin Cancer
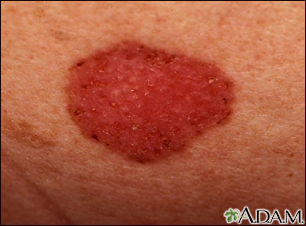
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a condition where abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably, often due to damage from sun exposure. There are several types of skin cancer, including basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, which is the most dangerous type.
Who’s at Risk for Skin Cancer?
Anyone can get skin cancer, but those with lighter skin, a history of sunburns, excessive sun exposure, a large number of moles, a family history of skin cancer, or a weakened immune system are at higher risk.
What Causes Skin Cancer?
The primary cause of skin cancer is ultraviolet (UV) light exposure, most often from the sun, but also from tanning beds. UV light can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to uncontrolled cell growth, which is cancer.
How Does Skin Cancer Start?
Skin cancer typically begins as a growth or abnormal patch of skin, often where the skin has been most exposed to the sun: the face, ears, neck, lips, and the backs of the hands. However, it can occur anywhere on the body.
What are the Symptoms of Skin Cancer?
Symptoms of skin cancer can include new, unusual growths or changes to existing moles. Basal cell carcinomas might look like a pearly or waxy bump or a flat, flesh-colored lesion. Squamous cell carcinomas might appear as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface. Melanomas can present various symptoms and often follow the ABCDE rule: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color that is not uniform, Diameter larger than the size of a pencil eraser, and Evolving size, shape or color.
How is Skin Cancer Diagnosed?
Skin cancer is typically diagnosed with a skin exam and a biopsy, where a sample of suspicious skin is removed and examined under a microscope.
How Can Skin Cancer be Treated?
Treatment for skin cancer depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer, as well as the patient's overall health. Options include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, photodynamic therapy (using drugs and light to kill cancer cells), and immunotherapy.
What Complications May Occur with Skin Cancer?
Potential complications of skin cancer include scarring, local recurrence, and, in the case of melanoma, it can spread (metastasize) to other parts of the body, which can be life-threatening.
How Can I Prevent Skin Cancer?
To prevent skin cancer, avoid excessive sun exposure, wear sun-protective clothing, regularly use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, and avoid tanning beds.
Long-term Management of Skin Cancer
Long-term management of skin cancer includes regular skin checks for any new or changing lesions, routine follow-up appointments with a dermatologist, and strict sun protection to prevent new skin cancers.
What is Recent Research Saying About Skin Cancer?
Recent research in skin cancer is investigating the genetics of skin cancer, new treatments for advanced skin cancer, and ways to improve sunscreen to better prevent skin cancer.
Where Can I Go For More Information on Skin Cancer?
For more information on skin cancer, you can visit websites like the American Academy of Dermatology, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), or the Skin Cancer Foundation.

