Rheumatoid Arthritis
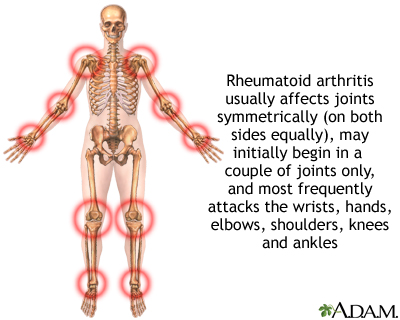
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects joints. It leads to painful swelling that can eventually result in joint deformity and bone erosion.
Who’s at Risk for Rheumatoid Arthritis?
While anyone can develop RA, it's more common in women and typically begins between the ages of 30 and 60. Risk factors include family history, smoking, obesity, and environmental exposures such as asbestos or silica.
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
The exact cause of RA is unknown, but it's believed to be a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. It is an autoimmune condition, meaning the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues.
How Does Rheumatoid Arthritis Start?
RA often starts gradually with fatigue, morning stiffness, and joint pain. Over time, joint inflammation and swelling may develop, often in smaller joints first such as those of the hands and feet.
What Are the Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Symptoms include tender, warm, and swollen joints, joint stiffness that's usually worse in the mornings, fatigue, fever, and weight loss. Symptoms may vary in severity and may even come and go.
How is Rheumatoid Arthritis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis of RA is based on patient symptoms, physical examination, and certain blood tests (like rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibodies). Imaging tests, such as X-rays or ultrasound, may be used to assess the degree of joint damage.
How Can Rheumatoid Arthritis Be Treated?
While there's no cure for RA, treatments aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), steroids, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), and physical therapy. In severe cases, surgery may be needed.
What Complications May Occur with Rheumatoid Arthritis?
RA can lead to complications such as osteoporosis, rheumatoid nodules, dry eyes and mouth, infections, abnormal body composition, carpal tunnel syndrome, heart problems, and lung disease.
How Can I Prevent Rheumatoid Arthritis?
While RA can't be prevented due to its genetic component, risk can be reduced by quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and eating a balanced diet.
Long-term Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Long-term management involves regular healthcare visits, adherence to treatment plans, and lifestyle modifications like regular exercise, balanced diet, and adequate rest.
What is Recent Research Saying About Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Recent research is focused on better understanding the genetic and environmental factors that trigger RA, and developing more effective treatments with fewer side effects. Some studies are exploring the potential of stem cell therapy and personalized medicine approaches.
Where Can I Go For More Information on Rheumatoid Arthritis?
For more information, visit reputable health websites like the American College of Rheumatology, the Arthritis Foundation, or the National Rheumatoid Arthritis Society.

