Prostate Cancer
What is Prostate Cancer?
Prostate cancer is a malignant growth that occurs in the prostate gland, a small, walnut-sized gland in men that produces seminal fluid. It is one of the most common types of cancer in men, and while some forms of prostate cancer grow slowly and may not cause significant problems, others can be aggressive and spread quickly.
Who's at risk for Prostate Cancer?
Men are at risk for prostate cancer, with the risk increasing with age. The majority of cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65. Other risk factors include a family history of prostate cancer, certain inherited gene mutations, and ethnicity, with African-American men having a higher risk compared to other racial groups.
What causes Prostate Cancer?
The exact cause of prostate cancer is not well understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Some gene mutations can increase the risk of developing prostate cancer, while other factors, such as a high-fat diet, smoking, and exposure to certain chemicals, may also play a role in its development.
How does Prostate Cancer start?
Prostate cancer begins with mutations in the DNA of prostate gland cells, causing them to grow and divide uncontrollably. Over time, these abnormal cells can form a tumor, which can invade nearby tissues and potentially spread to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or bloodstream.
What are the symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
In its early stages, prostate cancer may not cause any noticeable symptoms. As the cancer progresses, symptoms can include frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak or interrupted urine flow, blood in the urine or semen, pain or discomfort during urination or ejaculation, and persistent pain in the back, hips, or pelvis.
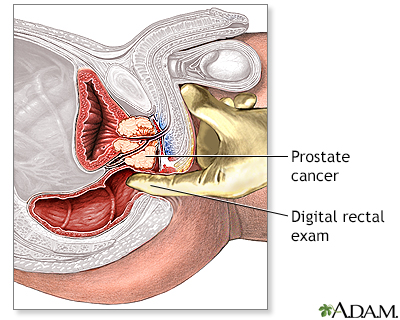
How is Prostate Cancer diagnosed?
Prostate cancer is often diagnosed through a combination of blood tests, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, and physical examinations, including a digital rectal exam. If these tests suggest the presence of cancer, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and determine the aggressiveness of the cancer.
How can Prostate Cancer be treated?
Treatment options for prostate cancer depend on the stage and aggressiveness of the cancer, as well as the patient's age and overall health. Options may include active surveillance, surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these treatments.
What complications may occur with Prostate Cancer?
Complications from prostate cancer can arise from both the cancer itself and its treatments. The cancer can spread to other parts of the body, causing pain and organ dysfunction. Treatment-related complications may include urinary incontinence, erectile dysfunction, bowel dysfunction, and side effects from medications or radiation therapy.
How can I prevent Prostate Cancer?
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk. This includes eating a balanced diet, rich in fruits and vegetables, maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking. Regular screening for prostate cancer can also help detect the disease early when it is most treatable.
Long-term management of Prostate Cancer
Long-term management of prostate cancer involves regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers to monitor the cancer's progress, assess treatment effectiveness, and manage any side effects or complications. It also includes maintaining a healthy lifestyle to support overall well-being and coping with any emotional or psychological challenges that may arise.
What is recent research saying about Prostate Cancer?
Recent research on prostate cancer has focused on improving early detection methods, identifying new genetic markers to predict cancer risk and aggressiveness, and developing targeted therapies to attack cancer cells more effectively while minimizing side effects. Additionally, researchers are investigating the potential benefits of immunotherapies and exploring how lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, may influence the development and progression of prostate cancer.
Where can I go for more information on Prostate Cancer?
For more information on prostate cancer, consult your healthcare provider or visit reputable websites like the American Cancer Society, the National Cancer Institute, or the Prostate Cancer Foundation.

