Menopause
What is menopause?
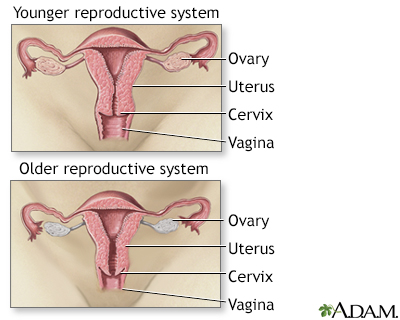
Menopause is a natural biological process that marks the end of a woman's reproductive years. It occurs when a woman has gone without a menstrual period for 12 consecutive months.
Who's at risk for menopause?
All women will eventually go through menopause, but certain factors can affect the timing of menopause, including:
- Age: Women typically go through menopause between the ages of 45 and 55, but it can occur earlier or later.
- Genetics: The age at which menopause occurs can be influenced by family history.
- Surgery: Women who have had their ovaries removed may go through menopause earlier than expected.
What causes menopause?
Menopause occurs when the ovaries stop producing eggs and the production of estrogen and progesterone declines.
How does menopause start?
Menopause typically starts with irregular periods, which can occur for several years before menstruation stops completely.
What are the symptoms of menopause?
Symptoms of menopause can vary from person to person, but may include:
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Sleep disturbances
- Mood changes
- Vaginal dryness
- Decreased libido
- Urinary problems
- Changes in skin and hair
- Weight gain
How is menopause diagnosed?
Menopause is typically diagnosed based on a woman's symptoms and medical history. Blood tests may also be used to measure hormone levels.
How can menopause be treated?
Treatment for menopause symptoms may include:
- Hormone replacement therapy: This involves taking estrogen and/or progesterone to replace the hormones that are no longer being produced by the ovaries.
- Non-hormonal therapies: Certain medications, such as antidepressants and blood pressure medications, may help relieve hot flashes and other symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes: Eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding smoking and alcohol may help manage menopause symptoms.
What complications may occur with menopause?
Complications of menopause may include:
- Osteoporosis: The decrease in estrogen production can lead to a loss of bone density and an increased risk of fractures.
- Heart disease: The risk of heart disease increases after menopause.
- Urinary incontinence: The decrease in estrogen production can lead to a weakening of the pelvic floor muscles, which can result in urinary incontinence.
How can I prevent menopause?
Menopause cannot be prevented, but healthy lifestyle choices, such as regular exercise and a healthy diet, may help manage menopause symptoms.
Long-term management of menopause
Long-term management of menopause involves ongoing treatment and monitoring for any complications that may develop.
What is recent research saying about menopause?
Recent research on menopause includes:
- A study published in 2020 found that women who experience hot flashes and night sweats during menopause may be at increased risk for cardiovascular disease.
- Researchers are also exploring new treatment options for menopause symptoms, such as non-hormonal therapies and lifestyle interventions.
Where can I go for more information on menopause?
The North American Menopause Society and the Mayo Clinic are both helpful resources for information on menopause. It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider for guidance and support in managing menopause.

