Hodgkin's Disease (Hodgkin's Lymphoma)
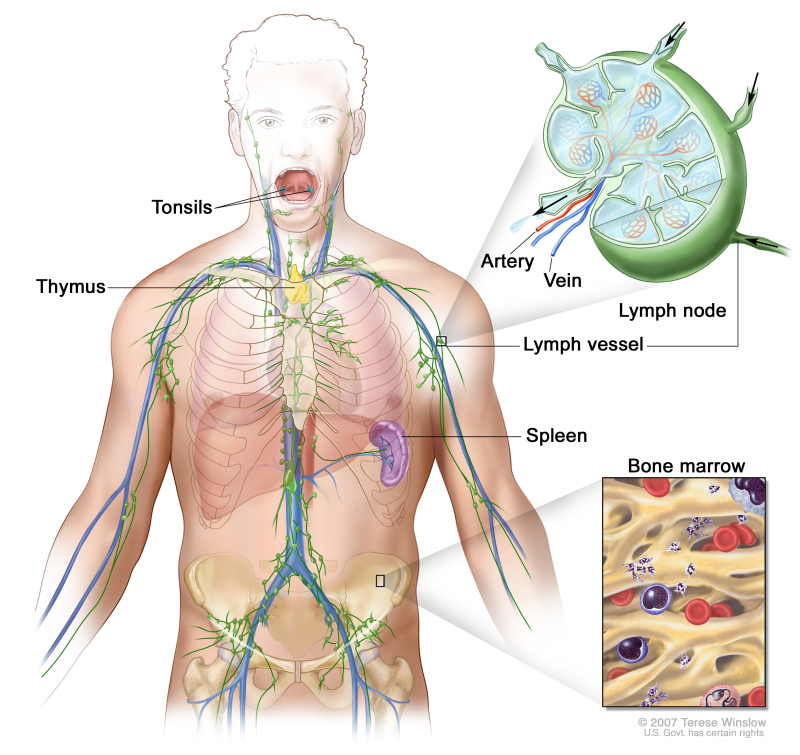
What is Hodgkin's Disease?
Hodgkin's disease, also known as Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system. The disease is characterized by the presence of abnormal cells called Reed-Sternberg cells, which multiply and form tumors in the lymph nodes.
Who's at risk for Hodgkin's Disease?
Hodgkin's disease can affect people of all ages, but it is most common in young adults between the ages of 15 and 40, and in older adults over the age of 55. Other risk factors for Hodgkin's disease include a family history of the disease, a weakened immune system, and exposure to the Epstein-Barr virus, which causes mononucleosis.
What causes Hodgkin's Disease?
The exact cause of Hodgkin's disease is not well understood, but it is believed to involve genetic mutations and environmental factors. In some cases, exposure to the Epstein-Barr virus has been linked to the development of Hodgkin's lymphoma.
How does Hodgkin's Disease start?
Hodgkin's disease begins when abnormal Reed-Sternberg cells develop in the lymphatic system. These cells multiply and form tumors, leading to the enlargement of lymph nodes and the disruption of normal immune system function.
What are the symptoms of Hodgkin's Disease?
Common symptoms of Hodgkin's disease include painless swelling of the lymph nodes, usually in the neck, armpits, or groin; fever; night sweats; unexplained weight loss; fatigue; and persistent itching. As the disease progresses, it may also cause more severe symptoms and complications.
How is Hodgkin's Disease diagnosed?
Hodgkin's disease is typically diagnosed through a physical examination, a review of your medical history, and imaging tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or PET scans. A definitive diagnosis is made through a biopsy of the affected lymph node, which involves removing a small sample of tissue for examination under a microscope.
How can Hodgkin's Disease be treated?
Treatment for Hodgkin's disease depends on the stage of the cancer and the overall health of the patient. Common treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and, in some cases, stem cell transplantation. In certain situations, surgery may be necessary to remove affected lymph nodes or other structures.
What complications may occur with Hodgkin's Disease?
Complications of Hodgkin's disease can include infections, anemia, and damage to the organs and tissues due to the spread of the cancer. Treatment-related complications, such as infertility, heart problems, and secondary cancers, may also occur.
How can I prevent Hodgkin's Disease?
There is no known way to prevent Hodgkin's disease, as the exact cause remains unclear. However, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can help support your overall health and reduce the risk of other types of cancer.
Long-term management of Hodgkin's Disease
Long-term management of Hodgkin's disease involves regular check-ups and monitoring by your healthcare team, as well as maintaining a healthy lifestyle to minimize the risk of complications and secondary cancers. Emotional support and counseling may also be beneficial for coping with the challenges of living with cancer.
What is recent research saying about Hodgkin's Disease?
Recent research on Hodgkin's disease has focused on understanding the genetic and environmental factors that contribute to its development, as well as improving treatment options and outcomes. Some studies have explored the use of targeted therapies, immunotherapies, and personalized treatment approaches based on the genetic makeup of the tumor. Additionally, researchers are investigating ways to reduce the long-term side effects of treatments and improve the quality of life for survivors.
Where can I go for more information on Hodgkin's Disease?
For more information on Hodgkin's disease, consult your healthcare provider or visit reputable health organizations' websites, such as the American Cancer Society (ACS), the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society (LLS), or the National Cancer Institute (NCI). These organizations provide comprehensive information on Hodgkin's disease, including prevention, treatment, management strategies, and ongoing research.

