Hemorrhoids
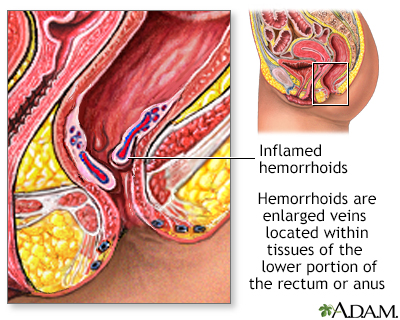
What are Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids, also known as piles, are swollen veins located in the lower rectum and around the anus. There are two types of hemorrhoids: internal hemorrhoids, which develop inside the rectum, and external hemorrhoids, which develop under the skin around the anus. Hemorrhoids can cause pain, itching, and discomfort, but they are usually not a severe health concern.
Who's at risk for Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids can affect people of all ages, but they are more common in adults over 50. Other factors that increase the risk of developing hemorrhoids include obesity, pregnancy, and chronic constipation or diarrhea. Additionally, people who often strain during bowel movements or spend long periods sitting on the toilet are more likely to develop hemorrhoids.
What causes Hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids are caused by increased pressure on the veins in the rectal and anal areas. This pressure can result from a variety of factors, such as constipation, diarrhea, pregnancy, obesity, and lifting heavy objects. Age can also play a role, as the tissues supporting the veins in the rectum and anus may weaken over time.
How do Hemorrhoids start?
Hemorrhoids begin when the veins in the rectum or anus become swollen and stretched due to increased pressure. This can cause the vein walls to bulge and become irritated, leading to the development of hemorrhoids.
What are the symptoms of Hemorrhoids?
Symptoms of hemorrhoids can vary depending on their location and severity. Common symptoms include pain, itching, or discomfort around the anus, swelling, and bleeding during bowel movements. In some cases, external hemorrhoids may form a painful clot, known as a thrombosed hemorrhoid.
How are Hemorrhoids diagnosed?
Hemorrhoids can usually be diagnosed through a physical examination and a review of your medical history. Your doctor may also perform a digital rectal exam or recommend additional tests, such as a colonoscopy, to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms.
How can Hemorrhoids be treated?
Treatment for hemorrhoids depends on their severity and the presence of any complications. Mild hemorrhoids can often be treated with over-the-counter remedies and lifestyle changes, such as increasing fiber intake, drinking plenty of water, and avoiding straining during bowel movements. More severe cases may require medical treatments, such as rubber band ligation, sclerotherapy, or surgery.
What complications may occur with Hemorrhoids?
While most hemorrhoids are not dangerous, complications can arise in some cases. These may include persistent pain, bleeding, and the development of anemia due to blood loss. In rare cases, an infected hemorrhoid may cause an abscess, which can require surgical treatment.
How can I prevent Hemorrhoids?
Preventing hemorrhoids involves reducing the factors that contribute to their development. Maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and adopt a diet high in fiber to help prevent constipation. Additionally, avoid spending excessive time on the toilet and do not strain during bowel movements.
Long-term management of Hemorrhoids
Managing hemorrhoids long-term involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a high-fiber diet, staying hydrated, and regular exercise. Over-the-counter creams and ointments can provide temporary relief from symptoms. In more severe cases, ongoing medical treatments or surgery may be necessary.
What is recent research saying about Hemorrhoids?
Recent research on hemorrhoids has focused on understanding their causes, improving treatment options, and finding ways to prevent their occurrence. Some studies have investigated the role of genetics in the development of hemorrhoids, while others have explored novel treatment methods, such as laser therapy and new surgical techniques.
Where can I go for more information on Hemorrhoids?
For more information on hemorrhoids, consult your healthcare provider or visit reputable health websites, such as the American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS), the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), or the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA). These organizations provide comprehensive information on hemorrhoids, including prevention, treatment, and management strategies.

