Cystic Fibrosis
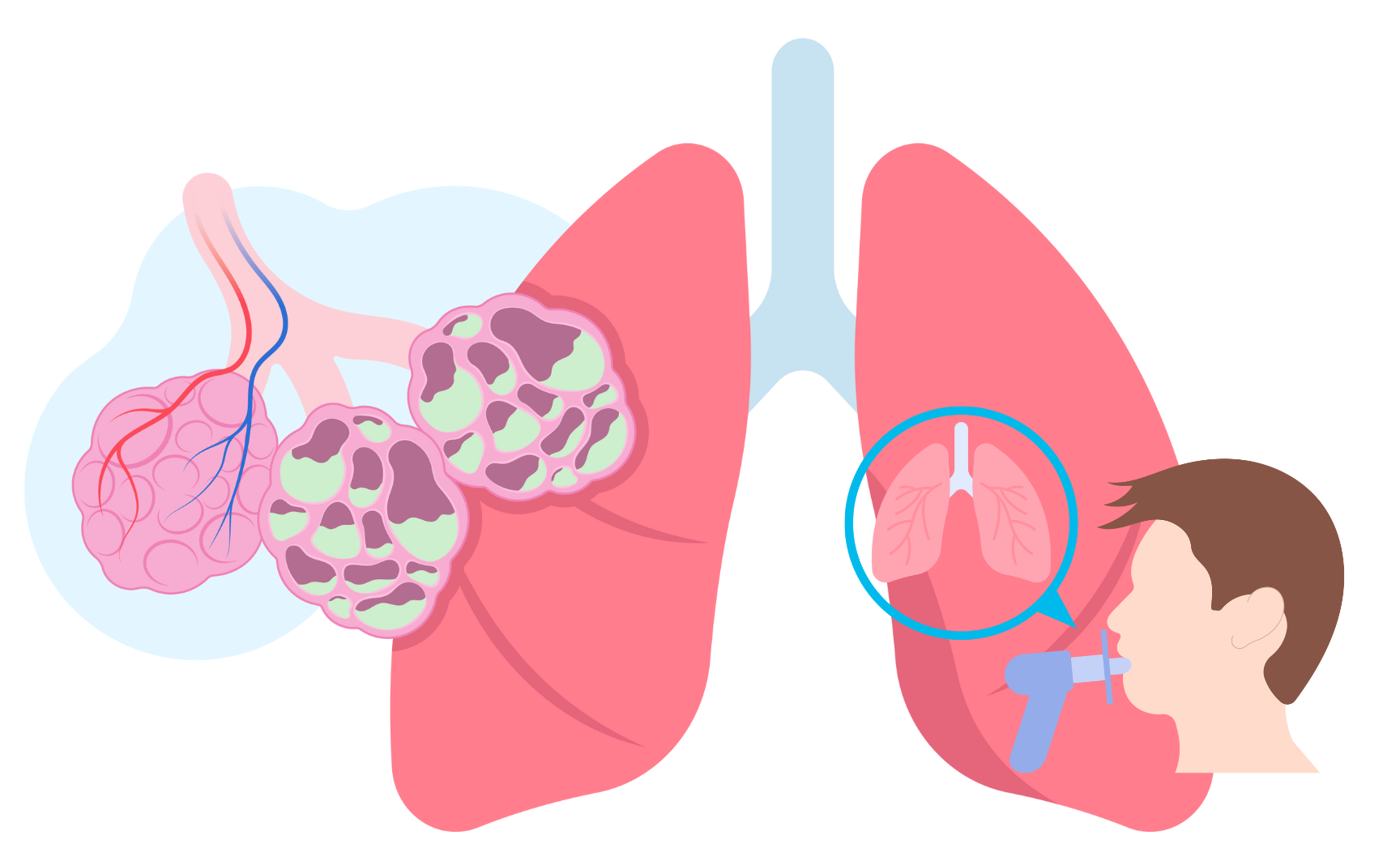
What is Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder that affects the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems, causing a buildup of thick mucus in the body.
Who’s at risk for Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited condition, and individuals with a family history of the condition or a history of certain genetic mutations may be at increased risk.
What causes Cystic Fibrosis?
Cystic fibrosis is caused by a mutation in the CFTR gene, which regulates the movement of salt and water in and out of cells. This mutation leads to a buildup of thick mucus in the body, which can impact multiple organ systems.
How does Cystic Fibrosis start?
Cystic fibrosis is present from birth, but symptoms may not become apparent until later in life. The condition can lead to a range of symptoms, including respiratory infections, digestive problems, and infertility.
What are the symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis?
The symptoms of cystic fibrosis can vary widely from person to person, but common symptoms may include:
- Persistent cough with thick mucus
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Difficulty breathing
- Stuffy nose
- Digestive problems, such as malabsorption and pancreatitis
- Infertility or reduced fertility
- Salty skin
How is Cystic Fibrosis diagnosed?
Cystic fibrosis is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests, such as genetic testing and sweat testing. Other tests, such as pulmonary function testing and imaging tests, may also be performed to assess lung function and identify other complications.
How can Cystic Fibrosis be treated?
Treatment for cystic fibrosis involves managing symptoms and preventing complications through a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and supportive care. Medications, such as antibiotics and bronchodilators, may be used to manage respiratory symptoms and prevent infections. Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding tobacco smoke, can also help improve overall health.
What complications may occur with Cystic Fibrosis?
Untreated cystic fibrosis can lead to serious complications, such as respiratory failure, liver disease, and infertility. The condition may also impact a person's quality of life, leading to social isolation, depression, and other mental health issues.
How can I prevent Cystic Fibrosis?
Preventing cystic fibrosis is not currently possible, as the condition is inherited. Genetic counseling and testing may be available for individuals who have a family history of the condition.
Long-term management of Cystic Fibrosis
Long-term management of cystic fibrosis involves ongoing monitoring of symptoms and regular follow-up with healthcare professionals. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses the specific needs of the person with cystic fibrosis.
What is recent research saying about Cystic Fibrosis?
Recent research has focused on identifying potential new treatments for cystic fibrosis, such as gene therapy and precision medicine approaches. There is also ongoing research into the effectiveness of different types of therapy for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
Where can I go for more information on Cystic Fibrosis?
The Cystic Fibrosis Foundation and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute provide up-to-date information on cystic fibrosis, including diagnostic criteria, treatment options, and ongoing research.

