Celiac Disease
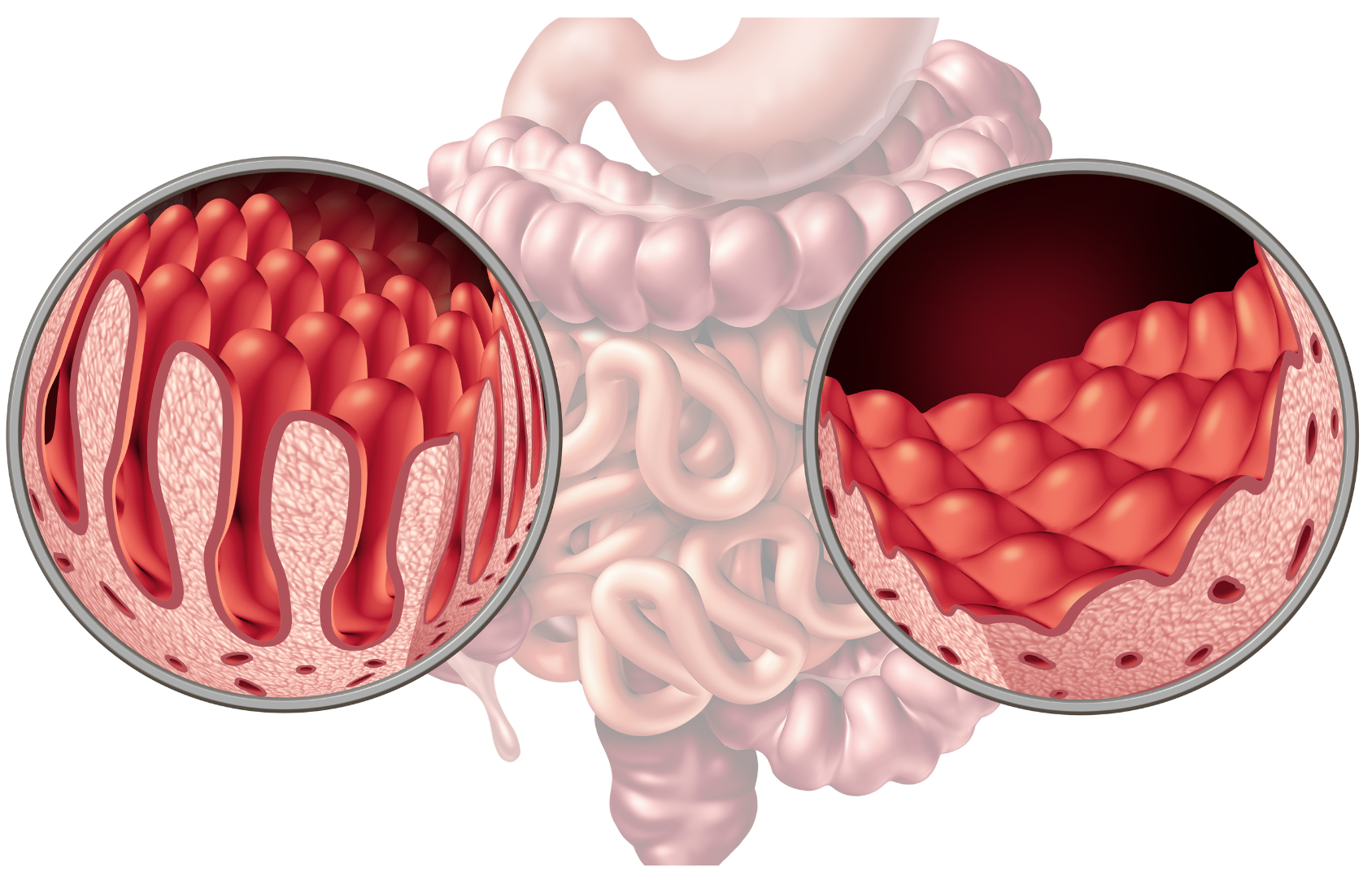
What is Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the digestive system. It is caused by a reaction to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, and can lead to damage of the small intestine and malabsorption of nutrients.
Who’s at risk for Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease can affect anyone, but it is more common in individuals who have a family history of the condition or who have other autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes or autoimmune thyroid disease.
What causes Celiac Disease?
Celiac disease is caused by an abnormal immune response to gluten, which leads to inflammation and damage of the small intestine. The exact cause of the abnormal immune response is not fully understood, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
How does Celiac Disease start?
Celiac disease can develop at any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed in children and adults in their 20s and 30s. The condition often begins with the onset of digestive symptoms, such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and bloating, after the consumption of gluten-containing foods.
What are the symptoms of Celiac Disease?
The symptoms of celiac disease can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms may include:
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
- Bloating
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Anemia
- Skin rash
- Joint pain
How is Celiac Disease diagnosed?
Celiac disease is diagnosed through a combination of blood tests and a biopsy of the small intestine. Blood tests can detect the presence of antibodies to gluten, while a biopsy can confirm the presence of damage to the lining of the small intestine.
How can Celiac Disease be treated?
The only effective treatment for celiac disease is a gluten-free diet, which involves avoiding all foods and products that contain gluten. This can be challenging, but it is essential for managing the condition and preventing complications.
What complications may occur with Celiac Disease?
Untreated celiac disease can lead to a range of complications, including malabsorption of nutrients, osteoporosis, infertility, and an increased risk of certain types of cancer.
How can I prevent Celiac Disease?
There is no known way to prevent celiac disease, but maintaining a healthy diet that is rich in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables may reduce the risk of developing the condition.
Long-term management of Celiac Disease
Long-term management of celiac disease involves ongoing adherence to a gluten-free diet, regular monitoring of symptoms, and follow-up with healthcare professionals. Nutritional counseling may also be recommended to ensure that individuals with celiac disease are meeting their nutritional needs.
What is recent research saying about Celiac Disease?
Recent research has focused on identifying new treatments for celiac disease, as well as exploring the role of genetics and the gut microbiome in the development of the condition. There is also ongoing research into the effectiveness of different types of gluten-free diets and the long-term outcomes of celiac disease.
Where can I go for more information on Celiac Disease?
The Celiac Disease Foundation and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases provide up-to-date information on celiac disease, including diagnostic criteria, treatment options, and ongoing research.

