Pharyngitis
What is Pharyngitis?
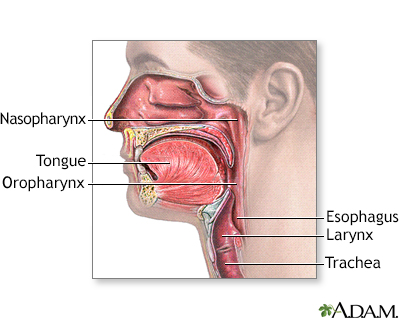
Pharyngitis, commonly known as sore throat, is the inflammation of the pharynx (throat), which is the part of the throat between the tonsils and the larynx (voice box). It is a common condition that affects people of all ages, and it can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection. The condition is common, especially among children and adolescents. Most cases of pharyngitis are caused by viral infections, but bacterial infections can also be the culprit. Pharyngitis can be acute, lasting for a short period, or chronic, lasting for several weeks or more.
Who’s at risk for Pharyngitis?
Anyone can develop pharyngitis, but some factors may increase the risk of developing the condition, including:
- Age: Children and adolescents are more susceptible to pharyngitis than adults.
- Exposure: People who are frequently exposed to viral or bacterial infections, such as healthcare workers or schoolteachers, are at a higher risk of developing pharyngitis.
- People with weakened immune systems
- Allergies: People with allergies or asthma may be more likely to develop pharyngitis.
- Smoking or exposure to smoke: Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke can irritate the throat and increase the risk of pharyngitis.
What causes Pharyngitis?
Pharyngitis can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection. The most common cause of pharyngitis is a viral infection, such as the common cold or the flu. Bacterial infections that can cause pharyngitis include streptococcus (strep throat), which is a common bacterial infection among children and adolescents, and other bacterial infections such as gonorrhea and chlamydia. Other causes include: Allergies and environmental irritants, such as cigarette smoke.
How does Pharyngitis start?
The starting symptoms of pharyngitis include sore throat, difficulty swallowing, redness and swelling of the tonsils and throat, fever, headache, and fatigue.
What are the symptoms of Pharyngitis?
The symptoms of pharyngitis can vary depending on the cause of the condition, but common symptoms may include:
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Redness and swelling in the throat (red and swollen tonsils)
- Swollen glands (lymph nodes) in the neck
- Fever
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Muscle aches
- Fatigue
- Runny nose
- Cough
- Hoarseness
How is Pharyngitis diagnosed?
Pharyngitis is typically diagnosed through a physical exam and a review of the patient's medical history. The doctor may also order additional tests, such as a throat culture or rapid strep test, to determine if the pharyngitis is caused by a bacterial infection.
How can Pharyngitis be treated?
The treatment for pharyngitis depends on the underlying cause of the condition. If the pharyngitis is caused by a viral infection, treatment typically involves self-care measures, such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter pain relievers. If the pharyngitis is caused by a bacterial infection, treatment may include antibiotics to help clear the infection. Other supportive treatments may include gargling with salt water and use of throat lozenges
What complications may occur with Pharyngitis?
In some cases, pharyngitis can lead to complications, such as:
- Tonsillitis and abcesses in the throat
- Sinusitis
- Difficulty breathing
- Middle ear infection
- Rheumatic fever (a rare complication of strep throat that can cause inflammation and damage to the heart, joints, and other organs)
- Kidney inflammation (glomerulonephritis). This is also called post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis, a kidney disease that can occur after streptococcal infections.
How can I prevent Pharyngitis?
There are several steps you can take to help prevent pharyngitis, including:
- Washing your hands frequently
- Avoiding close contact with people who are sick
- Covering your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing
- Avoiding sharing utensils or personal items, such as towels or toothbrush
- Quit smoking or avoid exposure to secondhand smoke
Long-term management of pharyngitis
- Practice good oral hygiene
- Stay hydrated
- Avoid smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Address any underlying allergies or environmental irritants that may be contributing to the condition
What is recent research saying about pharyngitis?
Recent research has focused on improving the accuracy of diagnosing streptococcal infections, which can cause pharyngitis. One study found that a molecular diagnostic test was more accurate than a traditional throat culture in detecting the bacteria that cause streptococcal infections.
Where can I go for more information on pharyngitis?
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery (AAO-HNS)

